Variability In Somatosensory Evoked Potential Test: Summing It Up
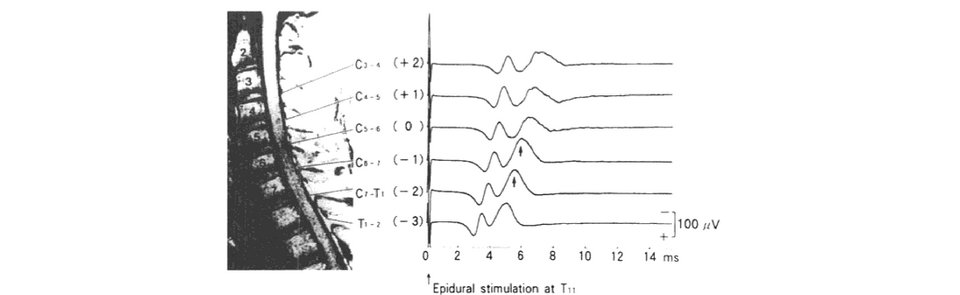
Somatosensory Evoked Potential Test Variability In my previous 2 post about temporal dispersion and somatosensory evoked potential test variability, I went over how to ID trial-to-trial variability, how to handle it and what was happening to the waveform. I'm going to...
Follow Up Post: SSEP Increased Variability vs. Increased Latency
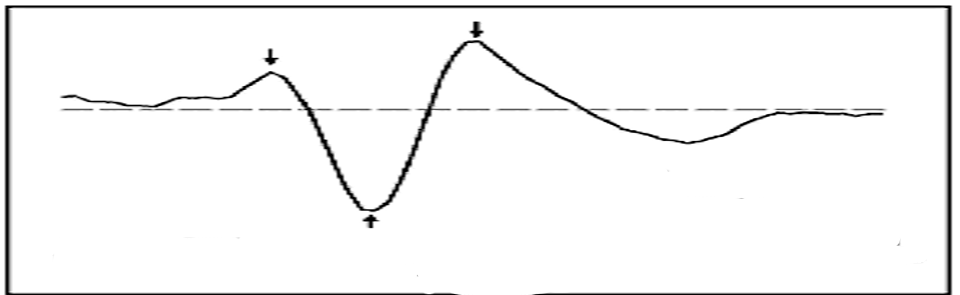
SSEP Increased Variability vs. Increased Latency: A question from a reader... In my last post, I talked about using the waterfall function to better determine your SSEP baselines, as well as how using it can be helpful in determining your level of confidence with the...
How To Handle Variable Intraoperative Somatosensory Evoked Potentials
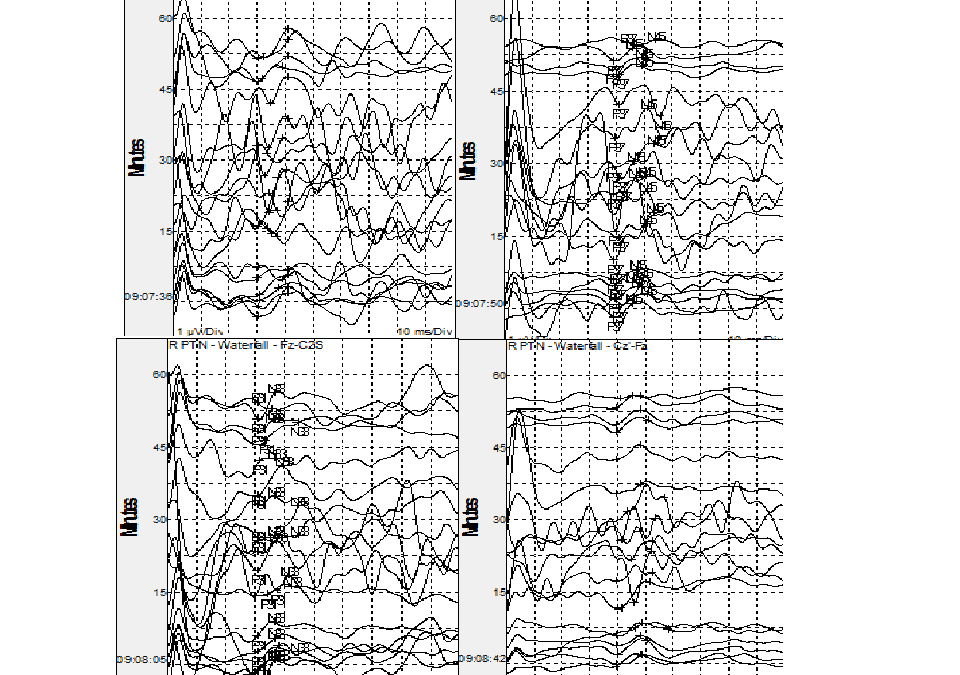
Intraoperative Somatosensory Evoked Potentials With our patient population getting older (the motor conduction slows by 0.4–1.7 m/s per decade after 20 years and the sensory by 2–4 m/s), overweight (conduction velocity of motor and sensory nerves decreases as BMI...

How To Get Your First Neuromonitoring Job: Q & A
Neuromonitoring Job Since I started this website, I get emails and calls all the time about how to get a neuromonitoring job with no CNIM. I'm glad to help, but feel like I end up saying a lot of the same thing over and over. So I'm making this post in hopes that...
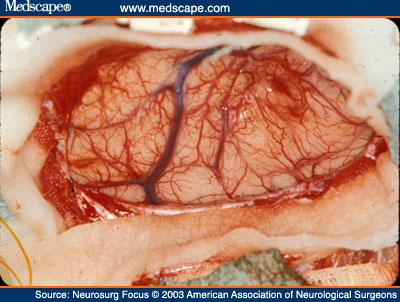
Intraoperative Monitoring For Gliomas… With Some New Toys
Glioma Surgery... Is Intraoperative Monitoring Wort It? Glioma tumors in the brain (which is a common malignant brain tumor) provides a intraoperative monitoring conundrum for the surgeon. Typically, can we offer the surgeon the ability to better localize the central...
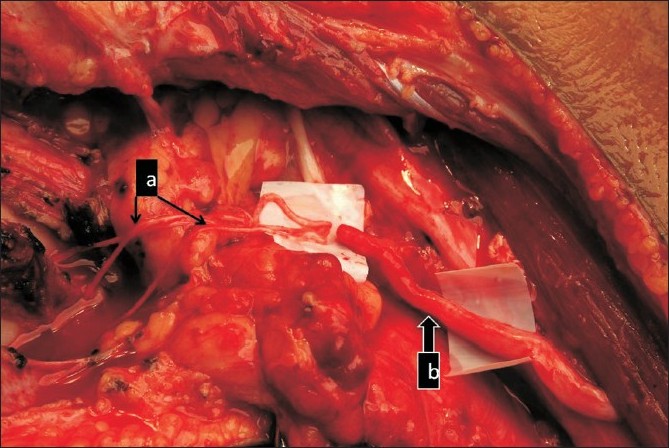
7 Ways To Assure Beutiful Intraoperative Nerve Action Potentials (NAP)
Intraoperative Nerve Action Potentials (NAP) Optimization Intraoperative nerve action potentials allow testing of the peripheral nerve through physiological means. A surgeon uses the information you give them from the NAP to assess nerve damage, assess the degree of...